British Troops Land in Boston to Maintain Order-1768
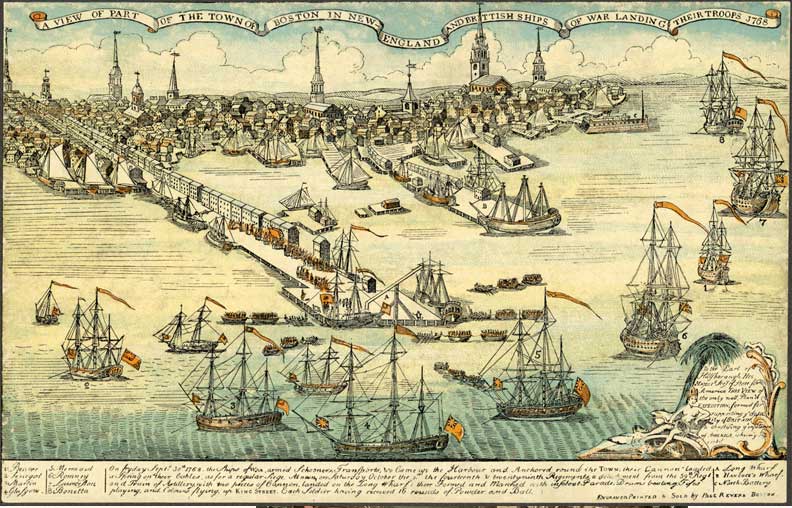
The actions of the colonist in response to the Townshend Act convinced the British that they needed troops in Boston to help maintain order. Lord Hillsborough, Secretary of State for the Colonies, dispatched two regiments-(4,000 troops), to restore order in Boston. The daily contact between British soldiers and colonists served to worsen relations.
The decision by the British to dispatch troops to Boston was one of their worst decisions, in an entire series of bad moves, that helped make the eventual independence of America inevitable. The British government reacted to the Americans, and specifically to the Massachusetts opposition to the Townshend Act, by dispatching troops to Boston. This might have been the correct policy if the opposition had been made up of just a few firebrands. The British, however, misread the opposition, which was widespread.
The announcement that British troops were arriving created immediate resentment among the colonists. The idea that British troops were coming not to defend the colonists in times of war, but to pacify them, seemed inconceivable to many. In addition, the idea that troops of the standing army, many of whom did not have a reputation for high moral standards, would be living in their city on a daily basis filled many Bostonians with dread.
At the end of September 1768, troop ships, accompanied by British men-of-war, arrived in Boston Harbor. The troops disembarked and initially encamped on the Boston Commons, as well as in the Court House and in Faneuil Hall. Friction immediately broke out when the governor offered the troops Manufactory House as a barracks. The inhabitants of the Manufactory House refused to be evicted, and the troops were forced to find other locations.
The British officers had no trouble finding lodging and being accepted into Boston society. This was not the case, however, with their soldiers. The British soldiers were consumers of both large quantities of rum and prostitutes. Both these activities were anathema to the rather Puritan population of Boston. Worse still was the harsh discipline meted out to British soldiers.
The British had a major problem with desertions. In the first few months of their stay in Boston, 70 troops deserted and found their way into the interior of the colony. Placing sentries on the outskirts of the city to stop deserters did nothing but inflame colonists further. Finally, General Gage, who had taken command of the British troops in Boston, ordered that the next deserters be captured and executed. That tragic fate fell on a young deserter named Ames. He was executed on the Boston Commons after an elaborate ceremony. This act disgusted the general population of Boston even more than the regular whipping of British soldiers in the same location for infractions against army rules.
The colonists’ views of the average British soldier varied from resentment to pity. However, while on duty, an almost guerrilla war seemed to rage between the soldiers and the colonists. This, of course, eventually resulted in the most well-known and tragic action, known as “the Boston Massacre.”
From the moment the British forces entered Boston to the moment they were forced by colonial troops to leave seven years later, their presence did the British no good. The extended British troop presence only served to bring the day of American independence closer.
 >
>