
|
|
 |
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
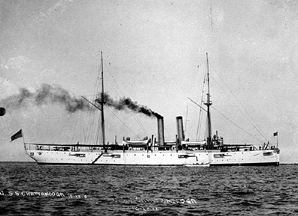
| Chattanooga II (C-16: dp. 3,200, 1. 308'10"; b. 44', dr. 16'9"; s. 16 k.; cpl. 339, a. 10 5", 8 6-pdr.; cl. Chattanooga) The second Chattanooga (C-16) was launched 7 March 1903 by Crescent Shipyard, Elizabethport, N.J.; sponsored by Miss L. N. Chambliss; completed at the New York Navy Yard, commissioned 11 October 1904, Commander A. Sharp in command; and reported to the Atlantic Fleet. Chattanooga's first cruise following shakedown was to the Caribbean, from which she returned to New York City to join the squadron which cleared for Cherbourg, France 18 June 1905. At Cherbourg, Olympia received on board the body of John Paul Jones, which the squadron brought home to the Naval Academy, arriving at Annapolis 23 July. Through the remainder of the year, Chattanooga aided in training men of the Maine and Massachusetts Naval Militia, and cruised briefly in the Caribbean. On 28 December she cleared San Juan, P.R., for the Suez Canal and duty in the Pacific. Between 29 April 1906, when she arrived at Cavite, P.I., and 10 August 1910, when she reported at Puget Sound Navy Yard for inactivation, Chattanooga joined the Asiatic Fleet in its winter operations in the Philippines and summer cruises to China, aiding in representing America's strength and interest in the Orient. Chattanooga was decommissioned at Puget Sound Navy Yard 17 September 1910. Chattanooga was placed in reserve commission 31 August 1912, remaining at Puget Sound, and in full commission 21 April 1914, for duty in Mexican waters. Through 1915 and 1916, she cruised to protect American interests from the disorder of the Mexican Revolution, and this duty continued after America's entrance into World War I until May 1917. Chattanooga then sailed through the Panama Canal for several months of patrol duties in the Caribbean, searching for German raiders. From July 1917, she escorted convoys from the Atlantic coast to rendezvous with other escorts in the approaches to French ports. This rugged duty across the stormy mid-Atlantic was broken only by two escort missions to Nova Scotia. Chattanooga took part in the Victory Fleet Review taken by the Secretary of the Navy ' in New York harbor 26 December 1918. After an overhaul, the cruiser carried a party of Liberian officials to Monrovia, then turned north for Plymouth, England, which she reached 7 May. As flagship of U.S. Naval Forces, European Waters, Chattanooga sailed among English and French ports until June. On 29 June, she served as leading honor escort guarding President Woodrow Wilson's departure from France in George Washington, then sailed on to call at German and Belgian ports before arriving in the Mediterranean for service as flagship for U.S Naval Forces, Turkish Waters. Cruising primarily in the Black Sea, she also served in the Adriatic in connection with the disposal of ships of the former Austrian Navy. From January through May 1921, she conducted regular patrols with the cruiser squadron assigned to European waters, and on 1 June, returned to the United States. She was decommissioned at Boston 19 July 1921, and laid up at Portsmouth Navy Yard until sold 8 March 1930. |
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
